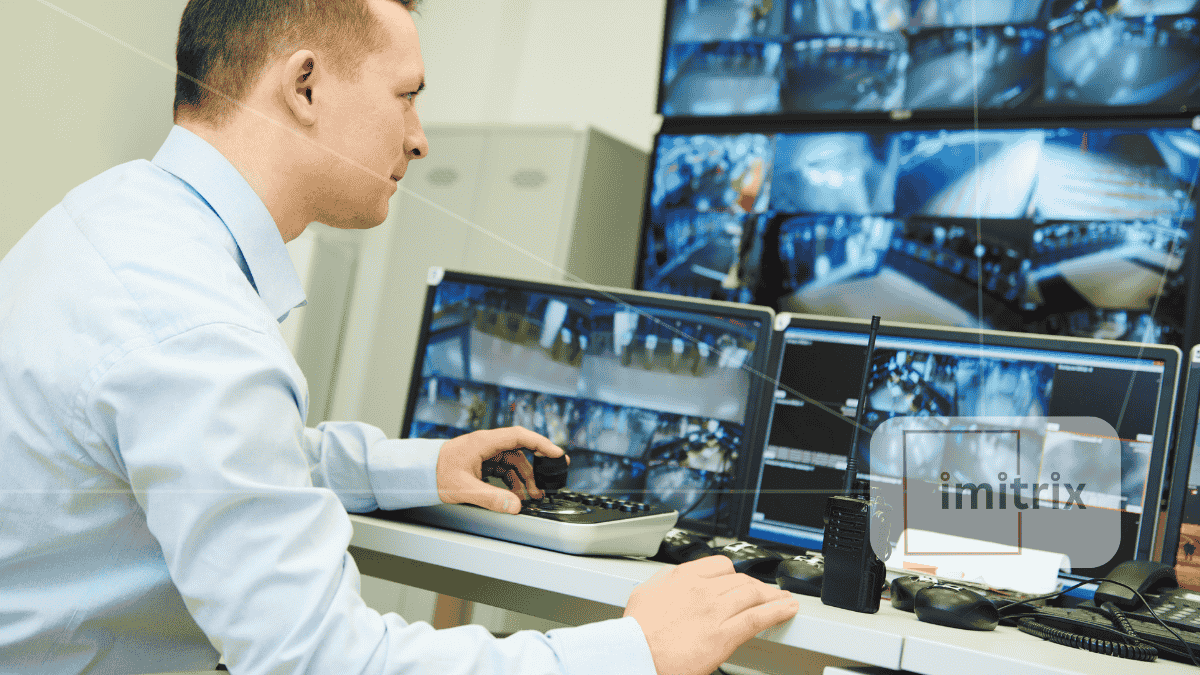
Telemedicine has evolved from a convenient healthcare alternative into a critical, sophisticated pillar reshaping care delivery. Artificial intelligence (AI) is central to this change, rapidly enhancing remote patient monitoring (RPM) capabilities. As a result, the broader telemedicine transformation is no longer optional; it’s setting a new standard for effective, efficient, and patient-centered care. This article explores how AI is driving this shift, the implications for healthcare providers and patients, and why this trend is truly transforming healthcare across the globe.
Understanding Telemedicine Transformation
Telemedicine transformation refers to the deep, structural shift in healthcare delivery through the adoption of digital technologies. It goes beyond virtual consultations to encompass remote diagnostics, continuous monitoring, personalized treatment, and real-time intervention. Artificial intelligence amplifies these capabilities, particularly in RPM, by interpreting complex data streams quickly and accurately.
Today, healthcare providers can oversee patients managing chronic conditions, recovering from surgery, or undergoing mental health treatment, all without requiring in-person visits. Devices such as wearable monitors, smart sensors, and mobile applications now collect critical health information. AI then turns this raw data into actionable insights, offering a richer, more dynamic understanding of each patient’s health trajectory.
How AI is Transforming Remote Patient Monitoring
AI dramatically improves remote patient monitoring by automating data gathering, analysis, and response mechanisms. Here’s how it’s reshaping RPM:
1. Predictive Analytics for Proactive Care
AI algorithms analyze real-time patient data to forecast potential health issues before they escalate. For example, machine learning models can detect subtle changes in heart rate variability, alerting medical teams to possible cardiac risks days before symptoms appear. This shift toward proactive care is a crucial part of the telemedicine transformation.
2. Crafting Highly Personalized Treatment Plans
AI leverages big data to tailor treatment strategies to each individual’s unique health profile. Rather than relying on generalized protocols, physicians can offer interventions precisely aligned with the patient’s biology, lifestyle, and history, continuously adjusting based on real-time feedback.
3. 24/7 Monitoring and Real-Time Alerts
Continuous monitoring powered by AI ensures that patients are never truly “alone.” If a patient’s vitals drift beyond a safe threshold, the system immediately notifies healthcare providers. This real-time responsiveness drastically reduces the risks associated with sudden health deterioration.
4. Reducing Avoidable Hospitalizations
Through predictive risk modeling, AI identifies patients most likely to experience complications, allowing early interventions that prevent unnecessary hospital admissions. This not only improves patient outcomes but also eases the burden on overwhelmed healthcare facilities.
5. Intelligent Data Summarization
AI condenses mountains of patient data into concise, meaningful reports. Clinicians receive only the most pertinent information, enabling quicker, more accurate decision-making without being bogged down by data overload.
Key Benefits for Patients and Healthcare Providers
The telemedicine transformation, propelled by AI, offers powerful advantages for both patients and providers.
For Patients:
- Accessibility: Patients in rural or underserved areas can access specialists without the need to travel.
- Convenience: Routine checkups can happen from home, reducing disruptions to daily life.
- Empowerment: Real-time health data gives patients a deeper understanding of their conditions, fostering greater engagement.
- Better Health Outcomes: Early intervention and personalized treatment directly correlate with improved health results.
For Providers:
- Operational Efficiency: AI streamlines administrative tasks like documentation and billing.
- Resource Optimization: Medical teams can prioritize critical cases while automating routine monitoring.
- Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy: Real-time insights from AI analytics aid in more precise diagnoses and treatment adjustments.
Challenges in the Telemedicine Transformation
Despite its immense promise, several challenges need addressing for a seamless telemedicine transformation.
Ensuring Data Privacy and Cybersecurity
As health data becomes increasingly digitized, robust security measures are vital. AI systems must comply with regulations like HIPAA, using encryption and anonymization to protect sensitive information.
Bridging the Digital Divide
Access to high-speed internet and smart devices remains uneven. Healthcare providers must advocate for inclusive solutions that ensure all patients can benefit from remote monitoring technologies.
Seamless Integration with Existing Systems
RPM tools must be compatible with current electronic health records (EHR) and hospital information systems. Poor integration can lead to data silos, missed information, and workflow inefficiencies.
Managing Ethical and Bias Concerns
AI models must be developed and tested to avoid biases that could disadvantage certain patient groups. Transparent algorithms and human oversight are crucial to maintaining fairness and equity in AI-driven healthcare.
Future Outlook: AI’s Expanding Role in Telemedicine Transformation
Looking ahead, the symbiosis between AI and telemedicine will only deepen. Several emerging trends will shape the future:
Advanced AI Diagnostics
AI will soon diagnose a broader spectrum of conditions using just remote data, potentially replacing initial in-person assessments for many non-emergency cases.
Smarter, More Versatile Wearables
Next-generation wearables will monitor an expanded range of metrics, including blood chemistry, hormonal fluctuations, and even early markers of neurological diseases, broadening the scope of telemedicine transformation.
Immersive Technologies
The integration of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) will enable remote examinations and virtual surgeries, making specialized care more widely available.
Mental Health Monitoring
AI is making strides in mental health, detecting changes in speech patterns, facial expressions, and online behavior to predict and prevent crises like depressive episodes or anxiety attacks.
Global Reach and Affordability
As technology costs decrease, telemedicine will expand into developing nations, dramatically improving global health outcomes and playing a critical role in transforming healthcare worldwide.
Case Study: AI-Powered Telemedicine in Action
A compelling example of AI’s impact is the partnership between Mount Sinai Health System and Current Health, an RPM platform. Using AI-driven analytics, they managed to reduce hospital admissions among heart failure patients by 30% within a year. Patients wore discreet devices that monitored vital signs continuously, while AI flagged at-risk individuals for early intervention. This real-world success underscores how telemedicine transformation, driven by AI, saves lives and reduces healthcare costs simultaneously.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence is not merely an enhancement; it is the engine powering the telemedicine transformation. By enabling proactive care, personalizing treatment, providing 24/7 monitoring, and reducing healthcare costs, AI is redefining how healthcare is delivered.
Yet challenges remain: cybersecurity, accessibility, integration, and ethical practices must stay front and center to ensure the benefits of AI reach every patient equitably.
Healthcare systems that embrace AI-driven RPM will stand out as leaders in a rapidly evolving landscape. They will not only improve patient care but also achieve operational excellence, embodying the goal of truly transforming healthcare for the better.
As AI technology advances and adoption widens, the telemedicine transformation will shift from innovative to indispensable, reshaping medicine into a more predictive, personalized, and patient-centered practice for generations to come.